What are STIs and STDs?
What causes and transmits STIs and STD s?
- Bacteria are single-celled organisms that can multiply rapidly and cause infections. Some of the common STIs caused by bacteria are chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and bacterial vaginitis. These STIs can be treated with antibiotics if diagnosed early.
- Parasites are small organisms that live on or in another organism and feed on its nutrients. Some of the common STIs caused by parasites are trichomoniasis, pubic lice, and scabies. These STIs can be treated with antiparasitic drugs or creams if diagnosed early.
- Viruses are tiny particles that invade the cells of a living organism and use them to reproduce. Some of the common STIs caused by viruses are human papilloma virus
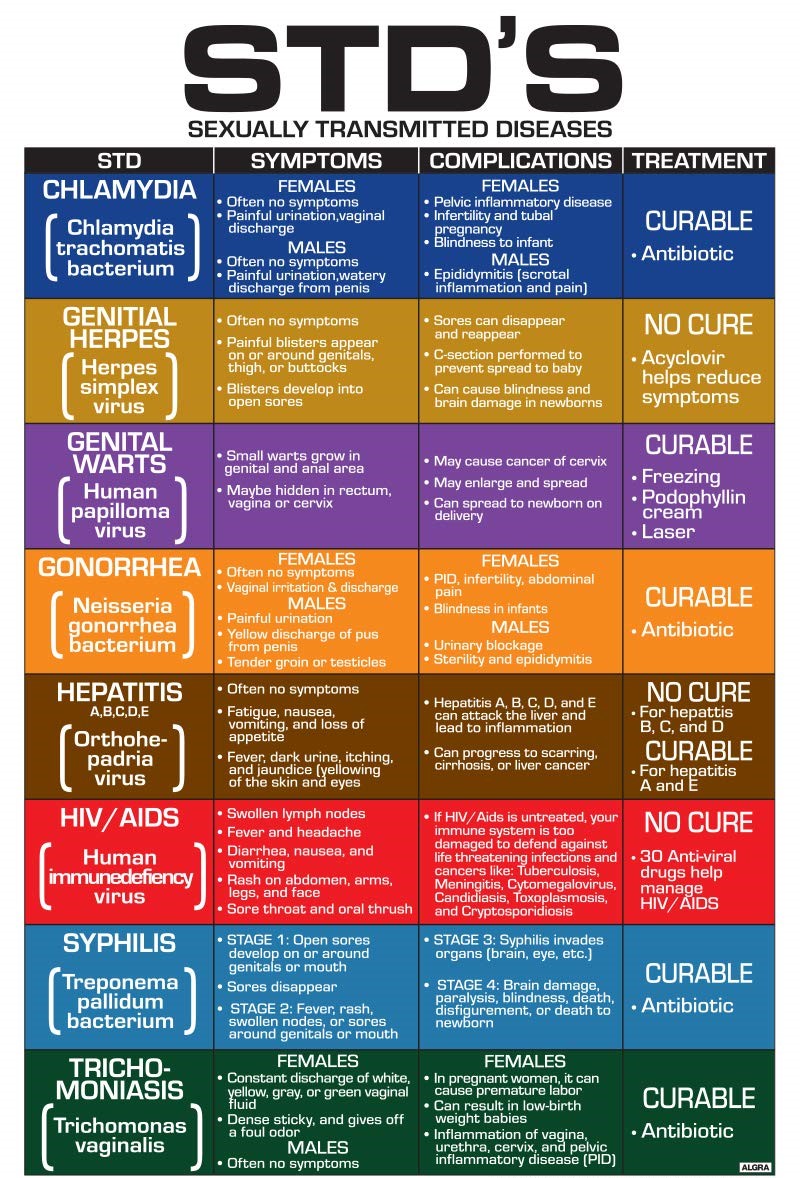
What are the symptoms and complications of STIs and STDs?
STIs and STDs can cause various symptoms and complications that affect the genital, oral, or anal areas of a person, as well as other parts of the body. Some of the common symptoms of STIs and STDs are:
- Sores or bumps on the genitals or in the oral or rectal area
- Painful or burning urination
- Discharge from the penis or vagina
- Unusual or odorous vaginal discharge
- Unusual vaginal bleeding
- Pain during sex
- Sore, swollen lymph nodes, particularly in the groin but sometimes more widespread
Some of these symptoms may be mild or unnoticed, while others may be severe or painful. However, it is important to note that some STIs and STDs may have no symptoms at all, or only show symptoms after a long period of time. Therefore, it is recommended to get tested regularly for STIs and STDs, even if you have no symptoms or feel healthy.
If left untreated, STIs and STDs can lead to serious complications that can affect the reproductive system, such as infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, ectopic pregnancy, and cervical cancer. They can also affect other organs and systems, such as the liver, brain, heart, eyes, and joints. Some STIs and STDs can also increase the risk of acquiring or transmitting HIV/AIDS, which can be fatal if not treated with antiretroviral therapy.
Prevention and Treatment of STIs and STDs
STIs and STDs are infections that can be transmitted through sexual contact. They can cause serious health problems if left untreated. Here are some ways to prevent and treat them:
- Avoid risky sexual behaviors such as having multiple partners, having unprotected sex, or sharing needles.
- Get tested regularly for STIs and STDs, especially if you have symptoms or a new partner. You can find testing sites near you at https://gettested.cdc.gov/Take antibiotics or antiviral medications as prescribed by your doctor if you are diagnosed with an STI or STD. Do not stop taking them until you finish the course, even if you feel better.
- Inform your sexual partners if you have an STI or STD, and encourage them to get tested and treated as well. This can help prevent further spread of the infection and complications
- Do not have sex until you and your partner are cured of the infection. This can help prevent reinfection and transmission to others.
